The rapid growth of smart cities worldwide has transformed urban living, making cities more connected, efficient, and data-driven. However, this digital transformation also brings significant security challenges. Smart city security frameworks are essential for safeguarding critical infrastructure, protecting personal data, and ensuring public safety. This article explores how these frameworks function and why they are crucial for modern urban environments.
The Rise of Smart Cities and the Need for Security
Smart cities leverage technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data to enhance urban services. However, the increased interconnectivity of devices and systems exposes cities to cyber threats, data breaches, and physical security risks. A robust security framework is necessary to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
Key Components of Smart City Security Frameworks
Smart city security frameworks consist of multiple layers, including cybersecurity, physical security, data privacy, and emergency response strategies. These components work together to create a secure and resilient urban ecosystem.
Cybersecurity in Smart Cities: Protecting Digital Infrastructure
Cybersecurity is a foundational element of smart city security. Cities must protect critical infrastructure such as power grids, transportation networks, and communication systems from cyberattacks. Measures like encryption, intrusion detection systems, and firewalls help safeguard digital assets.
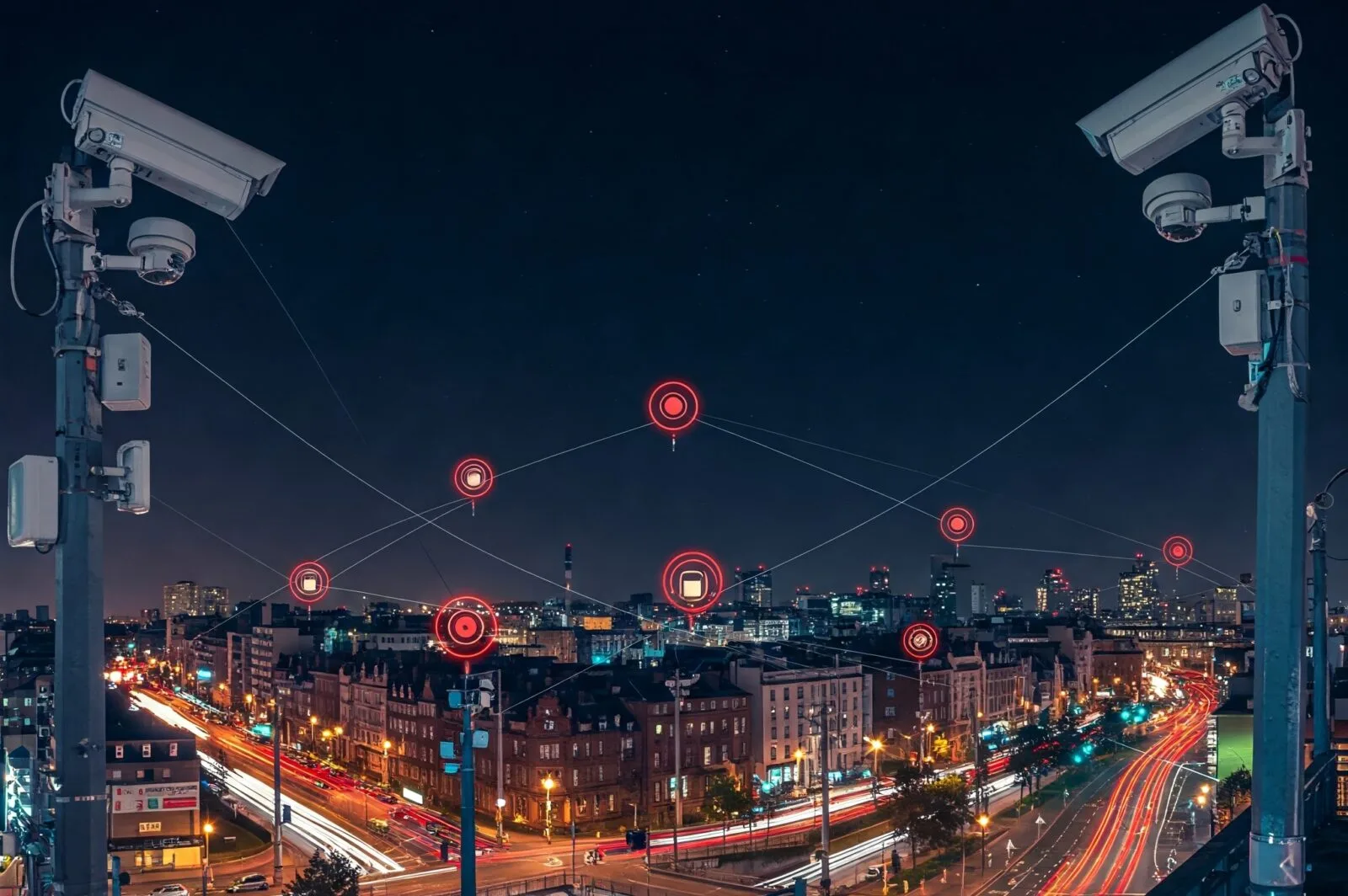
Physical Security Measures: Surveillance, Access Control, and Policing
Beyond digital security, smart cities also require robust physical security measures. Surveillance cameras, biometric access control, and smart policing strategies enhance public safety and reduce crime rates. Integrating AI-powered analytics improves real-time threat detection.
Data Privacy in Smart Cities: Ensuring Citizen Trust and Compliance
With vast amounts of data collected daily, smart cities must prioritize data privacy. Compliance with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and local data protection laws ensures that personal information remains secure. Implementing strict access controls and anonymization techniques enhances privacy.
AI and Machine Learning in Smart City Security
Artificial intelligence and machine learning play a crucial role in detecting security threats. AI-driven analytics can identify suspicious activities, predict potential cyber threats, and automate incident response, making security frameworks more proactive and efficient.
IoT Security: Safeguarding Connected Devices and Sensors
IoT devices, such as smart traffic lights and connected surveillance systems, are vulnerable to hacking. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, regular software updates, and network segmentation can mitigate IoT security risks.
The Role of Blockchain in Smart City Security Frameworks
Blockchain technology enhances transparency and security in smart cities by providing tamper-proof records. It helps secure transactions, identity verification, and data sharing while reducing the risk of fraud and cyberattacks.
Threat Detection and Response Strategies in Smart Cities
A well-defined threat detection and response strategy ensures that security incidents are quickly identified and mitigated. Implementing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and automated response mechanisms strengthens security resilience.
Emergency Preparedness and Crisis Management in Smart City Security
Smart cities must be prepared for emergencies such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, and infrastructure failures. AI-driven predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and automated alert systems enhance crisis management capabilities.
Public-Private Partnerships in Strengthening Smart City Security
Collaboration between governments, private organizations, and cybersecurity firms is essential for building secure smart cities. Public-private partnerships facilitate knowledge sharing, investment in security solutions, and coordinated incident response.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations for Smart City Security
Smart cities must comply with national and international security regulations. Establishing clear legal frameworks ensures accountability, protects citizen rights, and prevents unauthorized surveillance or data misuse.
Challenges in Implementing Smart City Security Frameworks
Despite technological advancements, implementing security frameworks in smart cities comes with challenges such as high costs, interoperability issues, and resistance to change. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach and continuous innovation.
Future Trends in Smart City Security and Emerging Technologies
The future of smart city security includes advancements in quantum encryption, biometric authentication, and AI-powered threat intelligence. As technology evolves, cities must stay ahead of emerging threats by adopting next-generation security solutions.
Case Studies: Successful Smart City Security Implementations
Several cities have successfully implemented comprehensive security frameworks. Examples include Singapore’s integrated command centers, Barcelona’s IoT-based security infrastructure, and New York City’s smart surveillance systems. These case studies highlight best practices and lessons learned.
How Citizens Can Contribute to Smart City Security
Citizen engagement is vital in maintaining urban security. Reporting suspicious activities, using secure digital services, and staying informed about cybersecurity best practices contribute to a safer city environment.
The Path Forward for Safer, Smarter Cities
Smart city security frameworks are essential for protecting urban environments from evolving threats. By integrating advanced technologies, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing data privacy, cities can ensure a safer and more resilient future for their residents. Investing in security today will enable the cities of tomorrow to thrive in an increasingly digital world.














Leave a comment