In today’s fast-paced digital world, keeping our information safe online is harder than ever. Cyber threats are always changing, becoming more complex and dangerous. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in. In 2025, AI is no longer just a futuristic idea; it’s a vital tool helping us fight against cybercriminals. It’s changing how we protect our data, detect attacks, and respond to threats, making our digital lives much more secure. Let’s discuss Role of Artificial Intelligence.
Table of Contents
Key Summary
- AI is Essential for 2025 Cybersecurity: With cyber threats growing smarter and faster, AI provides the advanced tools needed to defend against them effectively.
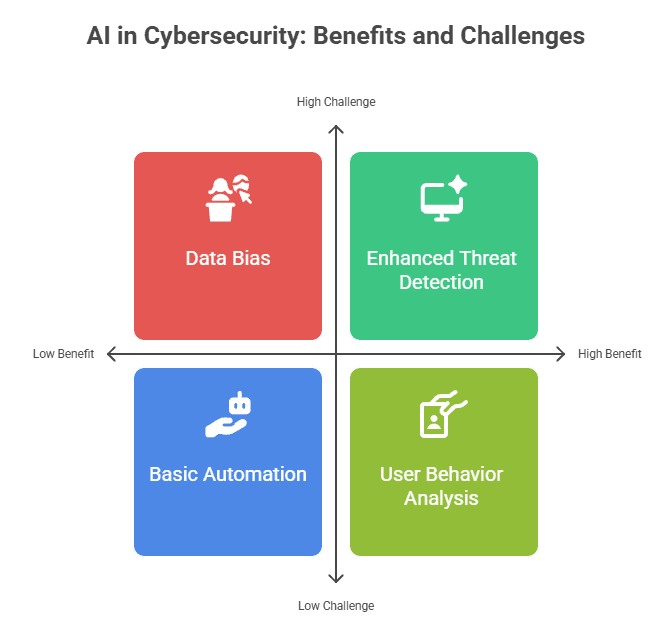
- Enhanced Threat Detection: AI can spot unusual patterns and new types of attacks much faster than humans, helping to prevent breaches before they cause major damage.
- Automated Response & Efficiency: AI automates many security tasks, from identifying vulnerabilities to responding to incidents, making cybersecurity teams more efficient and reducing human error.
- User Behavior Analysis: AI helps detect insider threats and compromised accounts by learning normal user behavior and flagging anything suspicious.
- Challenges Remain: While powerful, AI in cybersecurity still faces hurdles like data bias, adversarial AI (where attackers use AI), and the need for human oversight to make final decisions.
The Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape in 2025
The digital world of 2025 is a double-edged sword. On one side, we have amazing technology connecting us globally. On the other, cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit these connections. They use advanced methods like sophisticated phishing scams, ransomware that locks up your files, and stealthy malware that hides deep within systems.
The sheer volume of threats is overwhelming. Every second, countless attempts are made to breach systems, steal data, or disrupt services. Traditional security methods, which often rely on known signatures of threats, struggle to keep up with these rapidly evolving attacks. This is like trying to catch a speedy, shape-shifting monster with a slow, old net. The need for a smarter, faster defense mechanism has never been more critical.
How AI is Transforming Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence is changing the game in cybersecurity by bringing capabilities that were once unimaginable. Think of AI as a super-smart detective that can analyze massive amounts of information at lightning speed. It doesn’t just look for known bad guys; it learns what “normal” looks like and then quickly spots anything out of place. This allows it to find new threats that no one has seen before.
The role of Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity is to empower security systems to:
- Learn and Adapt: AI systems get smarter over time by analyzing data.
- Automate Tasks: It handles routine and complex tasks, freeing up human experts.
- Predict and Prevent: It can often foresee potential attacks before they happen.
This makes our defenses more proactive and less reactive, which is a huge step forward in protecting our digital assets.
Key Applications of AI in Cybersecurity
AI is being used in many exciting ways to boost our cybersecurity efforts. Let’s look at some of the most important applications in 2025.
1. Threat Detection and Prevention
One of AI’s biggest strengths is its ability to detect threats that traditional systems might miss.
- Anomaly Detection: AI learns the typical behavior of a network, users, and applications. If something unusual happens – like a user trying to access files they never normally touch, or a sudden surge of data leaving the network – AI flags it immediately. This helps catch zero-day attacks (new attacks no one knows about yet) and insider threats.
- Malware Analysis: AI can quickly analyze suspicious files to determine if they are malicious. It can look at the code, how the file behaves, and its characteristics to identify new strains of malware much faster than human analysts.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing past attack patterns and current trends, AI can predict where and how the next attacks might occur. This allows organizations to strengthen defenses in vulnerable areas proactively.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): AI-powered IDS can analyze network traffic in real-time, identifying suspicious activities and potential breaches with high accuracy.
“AI acts like a digital immune system, constantly scanning, learning, and reacting to protect our valuable data from unseen dangers.”
Many of these advanced tools, while complex, build upon core security principles. Understanding even the best free cybersecurity tools can provide a foundation for appreciating how AI enhances these capabilities.
2. Automated Incident Response
When a cyberattack happens, every second counts. AI can significantly speed up the response process.
- Rapid Triage: AI can quickly assess the severity of an incident, prioritizing the most critical threats.
- Automated Actions: For known threats, AI can automatically take actions like isolating infected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or patching vulnerabilities without human intervention. This is a crucial aspect of automated cybersecurity incident response.
- Guided Response: For more complex incidents, AI can provide security analysts with detailed information and recommended steps, helping them make faster, more informed decisions.
This automation reduces the time attackers have to cause damage and frees up human experts to focus on the most complex problems.
3. Vulnerability Management
Finding and fixing weaknesses (vulnerabilities) in systems is a never-ending task. AI helps make this process smarter.
- Continuous Scanning: AI-powered tools can constantly scan systems and applications for new vulnerabilities.
- Prioritization: Not all vulnerabilities are equally dangerous. AI can analyze the potential impact and likelihood of exploitation for each vulnerability, helping teams prioritize which ones to fix first. This is a key step in learning how to conduct a cyber risk assessment.
- Configuration Analysis: AI can check system configurations to ensure they meet security best practices and identify misconfigurations that could lead to breaches.
4. User Behavior Analytics (UBA)
People are often the weakest link in security. AI helps by monitoring user behavior.
- Baseline Behavior: UBA systems use AI to learn what “normal” activity looks like for each user and group.
- Insider Threat Detection: If an employee suddenly tries to access sensitive files they don’t usually need, or logs in at unusual hours, AI will flag this. This helps catch malicious insiders or compromised accounts.
- Account Compromise Detection: If an attacker gains access to a user’s account, AI can often spot the change in behavior (e.g., accessing different resources, from a new location) and alert security teams.
5. Security Operations Center (SOC) Enhancement
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) are the command centers for cybersecurity. AI helps them run more smoothly.
- Reducing Alert Fatigue: SOC analysts are often swamped with thousands of alerts daily. AI can filter out false positives and group related alerts, presenting analysts with only the most critical and actionable information.
- Faster Investigations: AI can correlate data from various sources (firewalls, endpoints, applications) to provide a complete picture of an incident, drastically speeding up investigation times.
- Threat Intelligence: AI can process vast amounts of global threat intelligence, identifying new attack campaigns and indicators of compromise (IOCs) to strengthen defenses.
6. Phishing and Social Engineering Defense
Phishing attacks, where criminals trick people into giving up information, are incredibly common. AI is getting better at spotting them.
- Email Analysis: AI can analyze email content, sender reputation, links, and attachments to identify sophisticated phishing attempts that might bypass traditional filters.
- Language and Context: AI can understand the context and language used in emails to detect subtle signs of social engineering.
- Proactive Warnings: Some AI systems can even warn users about suspicious emails or websites before they interact with them.
It’s crucial to remember that clicking on suspicious links or downloading unofficial software, often associated with things like the hidden costs of pirated downloads, can open doors for these attacks. AI helps detect these risks.
Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
The role of Artificial Intelligence brings several significant advantages to modern cybersecurity efforts:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed & Efficiency | AI processes data and detects threats far faster than humans, allowing for near real-time responses to attacks. |
| Accuracy | AI can identify complex patterns and anomalies with high precision, reducing false positives and focusing on real threats. |
| Scalability | AI systems can handle massive amounts of data and monitor vast networks, scaling up or down as needed without human limitations. |
| Proactive Defense | By learning and predicting, AI helps organizations move from reacting to threats to actively preventing them. |
| Reduced Human Error | Automating routine tasks minimizes mistakes that humans might make, ensuring consistent security measures. |
| Cost Savings | While initial investment can be high, AI can reduce operational costs by automating tasks and preventing costly breaches. |
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its impressive capabilities, AI in cybersecurity isn’t a magic bullet. There are still challenges to overcome.
- Bias in Data: AI systems learn from the data they are fed. If this data is biased or incomplete, the AI might make incorrect decisions, leading to missed threats or false alarms.
- Adversarial AI: Cybercriminals are also using AI. They can develop “adversarial attacks” designed to trick AI-powered security systems, making it a constant AI vs. AI battle.
- Cost and Complexity: Implementing and maintaining advanced AI cybersecurity solutions can be expensive and require specialized expertise, which might be a barrier for smaller organizations.
- Need for Human Oversight: AI is a powerful tool, but it lacks human intuition, ethical judgment, and the ability to understand complex, nuanced situations. Human experts are still essential for making final decisions, especially in critical incidents.
- Explainability: Sometimes, it’s hard to understand why an AI made a certain decision (the “black box” problem). This can make it difficult to trust or audit AI-driven security actions.
Even with AI’s help, having a solid plan for how to prepare for a cyber attack remains crucial. AI enhances our tools, but human strategy and readiness are still paramount.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity (Beyond 2025)
Looking beyond 2025, the role of Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity will only grow. We can expect to see:
- More Autonomous Systems: AI will take on even more decision-making roles, responding to threats with minimal human intervention, especially for well-understood attack types.
- AI-Driven Deception: AI could be used to create decoy systems and fake data to trap attackers, learning their methods without risking real assets.
- Quantum Computing’s Impact: As quantum computing advances, it will pose new encryption challenges, and AI will be vital in developing new quantum-resistant security measures.
- Ethical AI: More focus will be placed on developing ethical AI in security, ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in its decisions.
- Closer Human-AI Collaboration: The future isn’t about AI replacing humans, but about a powerful partnership where AI handles the heavy lifting, and humans provide strategic oversight and creativity.
Let’s take some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is AI replacing cybersecurity jobs?
Not at all. It’s a tool that automates the mundane tasks, freeing up human experts to focus on the truly difficult, strategic work that requires human judgment.
How does AI spot a threat no one has seen before?
It learns what is “normal” for your network. Anything that deviates from that established pattern is flagged as suspicious, even if it’s a brand-new attack.
What if cybercriminals use AI too?
This is a real and growing challenge. It creates a constant technological battle between defensive AI and adversarial AI. This is a key reason why human experts are still indispensable—to out-think the enemy’s AI.
Can I trust an AI to make critical security decisions?
AI is great for fast, automated actions on known threats. For critical, complex incidents, it’s best used to provide detailed information and recommended steps, with the final decision resting with a human expert.
Is AI in cybersecurity only for big companies?
No. AI is increasingly integrated into consumer-level security products, from antivirus software to home routers, making advanced protection accessible to everyone.
Bottom Line
In 2025, Artificial Intelligence is not just an add-on; it’s a fundamental pillar of modern cybersecurity. It has revolutionized how we detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats, making our digital environments safer and more resilient. While challenges remain, the ongoing development and integration of AI promise an even more secure future. By understanding and embracing the role of Artificial Intelligence, organizations and individuals can better protect themselves in an increasingly connected and dangerous digital world.















Leave a comment