In today’s hyperconnected world, cybersecurity has become the foundation of digital trust. As organizations face an ever-growing number of cyber threats, from data breaches to ransomware attacks, the need for innovative defense mechanisms has skyrocketed. Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI)—a game-changing force in the fight against cybercrime. Discover how AI is transforming the field of cybersecurity in our comprehensive exploration, “Is AI Used in Cybersecurity? Let’s Understand in Depth.” Learn about its applications in threat detection, automated responses, and user behavior analytics, and understand the benefits and challenges of integrating AI into security strategies.
Overview
AI is revolutionizing cybersecurity by automating threat detection, predicting vulnerabilities, and improving the speed and precision of incident responses. With its ability to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time and detect patterns humans might overlook, AI empowers organizations to stay one step ahead of even the most sophisticated cyberattacks. Let’s understand the key facts about Is AI Used in Cybersecurity?
Purpose
This blog will explore the practical applications of AI in cybersecurity, showcasing how it is transforming threat detection, user behavior analysis, incident response, and more. Along the way, we’ll uncover its benefits and the critical role it plays in safeguarding digital systems.
1. Is AI Used in Cybersecurity?
Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity refers to the use of intelligent algorithms and machine learning models to identify, prevent, and mitigate cyber threats. Unlike traditional security tools that rely on static rules, AI leverages dynamic data analysis and self-learning to adapt to new and evolving threats in real-time.
Role of AI as a Cybersecurity Tool: AI serves as a powerful ally in enhancing threat detection, prevention, and response:
- Threat Detection: AI scans massive volumes of data to uncover hidden patterns and anomalies, enabling the identification of potential security breaches before they cause harm.
- Threat Prevention: By analyzing historical attack data, AI systems can predict vulnerabilities and guide organizations in shoring up their defenses proactively.
- Incident Response: When a breach occurs, AI can automate responses, such as isolating compromised systems or neutralizing malicious actors, reducing the impact of attacks.
AI is not just a tool—it’s a vital component of modern cybersecurity strategies, ensuring faster, smarter, and more effective protection against digital threats.
2. Key Applications of AI in Cybersecurity
Discover the key applications of AI in cybersecurity, from advanced threat detection and automated incident response to predictive analytics and user behavior analysis. Let’s understand how AI is enhancing security measures, reducing response times, and improving overall defense strategies against evolving cyber threats. Following are some major key applications.
a. Threat Detection and Prevention
AI has redefined how organizations identify and prevent cyber threats. Traditional methods often rely on signature-based detection, which can be ineffective against new or evolving attacks. AI, however, uses advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets in real time, identifying unusual patterns or anomalies that may signal a cyber threat. For example, AI-powered systems monitor network traffic and user activity to detect deviations from normal behavior. When potential threats are identified, they trigger real-time alerts, enabling security teams to respond swiftly and effectively.
b. User Behavior Analytics
AI-driven user behavior analytics creates a baseline of typical user activity within an organization. By employing deep learning techniques, these systems can detect subtle deviations from normal behavior, such as unusual login times or access to sensitive files. This proactive approach allows organizations to catch potential insider threats or compromised accounts before significant damage occurs. Over time, AI systems refine their models, improving accuracy and adapting to changes in user behavior.
c. Automated Incident Response
One of AI’s most valuable contributions is the ability to automate incident response. When a security breach is detected, AI can initiate pre-programmed actions like isolating affected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or notifying relevant personnel. This automation minimizes response times and reduces the window of opportunity for attackers. By streamlining incident management, AI ensures that cybersecurity teams can focus on more complex challenges while routine tasks are handled efficiently.
d. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
AI enhances identity and access management by continuously analyzing user login patterns and access behavior. For example, if a user logs in from an unusual location or device, AI can flag the activity and enforce additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication or access suspension. This capability helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures that only verified users can access critical systems.
e. Vulnerability Management
AI excels in identifying vulnerabilities within an organization’s infrastructure by analyzing system logs, configurations, and historical attack data. These tools can prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact, allowing organizations to address the most critical weaknesses first. This predictive approach not only improves overall security but also optimizes resource allocation.
f. Predictive Analytics
Using historical data, AI can anticipate future cyber threats before they occur. By identifying patterns associated with past attacks, AI systems provide security teams with actionable insights into potential risks. This proactive approach enables organizations to implement preventative measures, effectively staying ahead of emerging threats.
g. Enhancing Security Operations Center (SOC) Efficiency
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) often deal with an overwhelming number of alerts, many of which turn out to be false positives. AI reduces this burden by intelligently categorizing and prioritizing alerts based on their severity and likelihood of being genuine threats. This allows analysts to focus on critical incidents, improving efficiency and reducing alert fatigue.
3. Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
In the above section, we explored the key application of cybersecurity now let’s understand the benefits of bringing AI to the cybersecurity landscape. From improving threat detection and preventing data breaches to automating incident responses and enhancing security operations, AI empowers organizations to strengthen their defense mechanisms. With its ability to analyze vast amounts of data in real time, AI not only boosts efficiency but also enables proactive measures, reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
a. Faster Threat Detection
One of the most significant advantages of AI in cybersecurity is its speed. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying threats far quicker than traditional methods or human analysts. This rapid detection allows organizations to act promptly, reducing the potential damage caused by cyberattacks.
b. Proactive Defense
AI enables organizations to adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity by predicting potential threats and vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. By analyzing historical attack patterns and identifying areas of weakness, AI helps businesses fortify their defenses, ensuring they are prepared for future challenges.
c. Reduced Human Error
Human error is one of the leading causes of security breaches. AI minimizes this risk by automating many aspects of cybersecurity, such as monitoring systems, detecting anomalies, and responding to incidents. By removing the need for manual intervention in routine tasks, AI ensures more consistent and reliable security outcomes.
d. Scalability
As organizations grow, so do their cybersecurity challenges. AI offers scalability by efficiently managing and protecting large and complex systems without requiring a proportional increase in human resources. Whether monitoring thousands of endpoints or analyzing terabytes of data, AI provides a scalable solution to meet the demands of modern cybersecurity.
e. Improved Incident Response
AI streamlines incident response by automating critical tasks, such as isolating compromised systems or blocking malicious activities. This reduces response times and minimizes the impact of security breaches. Furthermore, AI’s ability to provide detailed insights into the nature of an attack allows cybersecurity teams to implement more effective countermeasures.
f. Cost Efficiency
While implementing AI-based cybersecurity solutions may require an upfront investment, the long-term cost savings are significant. By reducing the need for manual monitoring, improving efficiency, and minimizing the financial impact of successful cyberattacks, AI delivers a strong return on investment for organizations.
g. Enhanced Accuracy and Precision
AI systems excel in identifying threats with a high degree of accuracy, reducing false positives and false negatives. This precision ensures that security teams can focus their efforts on genuine threats, improving overall efficiency and effectiveness.
h. Adaptability to Evolving Threats
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, making traditional static defenses insufficient. AI’s self-learning capabilities allow it to adapt to new attack methods, ensuring that cybersecurity defenses remain effective in an ever-changing threat landscape.
4. Challenges of Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
Implementing AI in cybersecurity presents several challenges. High initial costs, complex system deployment, and the need for specialized knowledge can strain resources. AI’s reliance on quality data means poor data can lead to ineffective threat detection. Additionally, there is the risk of AI being exploited by cybercriminals or introducing ethical concerns such as privacy and bias. Let’s discuss this in brief.
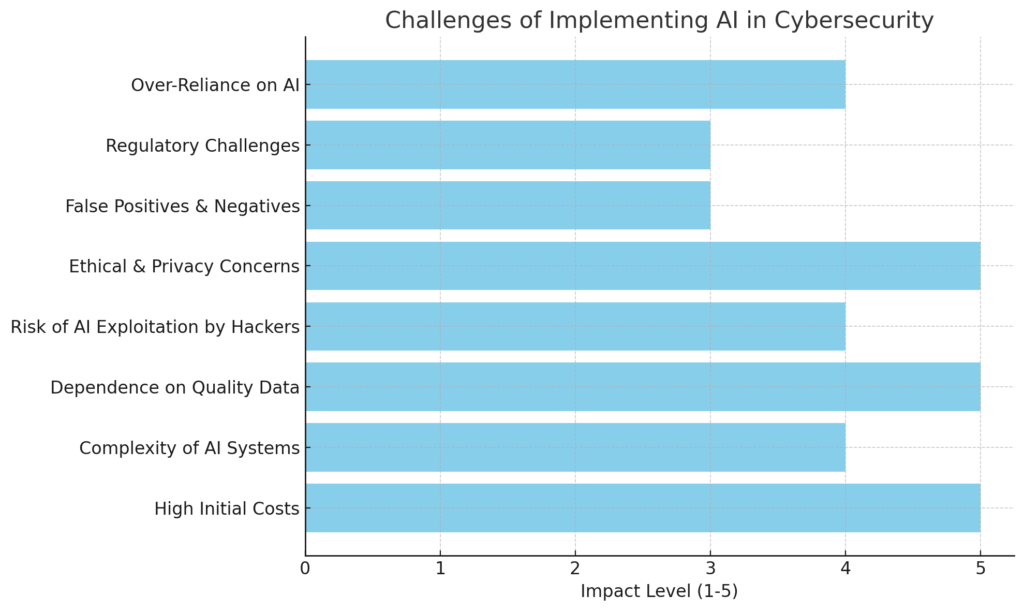
a. High Initial Costs
Integrating AI into cybersecurity requires a significant investment in terms of technology, infrastructure, and expertise. Many organizations, especially smaller businesses, may find it challenging to allocate the necessary resources to implement AI-based solutions.
b. Complexity of AI Systems
AI systems are highly sophisticated and require specialized knowledge to develop, implement, and maintain. Organizations often need to hire skilled professionals or provide extensive training for their existing teams, which can increase both costs and complexity.
c. Dependence on Quality Data
The effectiveness of AI systems depends heavily on the quality and quantity of data they are trained on. Inaccurate, incomplete, or biased data can lead to poor decision-making and vulnerabilities in cybersecurity defenses. Ensuring access to reliable and up-to-date data is a critical challenge for many organizations.
d. Risk of AI Exploitation by Hackers
While AI strengthens cybersecurity defenses, it can also be leveraged by cybercriminals to launch more sophisticated attacks. Hackers can use AI to create more effective phishing campaigns, evade detection, or exploit vulnerabilities in AI-based security systems. This ongoing arms race between defenders and attackers highlights the need for constant innovation.
e. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
AI systems often require access to large amounts of sensitive data to function effectively. This raises concerns about privacy and data protection, especially when dealing with personal or confidential information. Organizations must ensure compliance with data protection laws and ethical considerations when implementing AI in cybersecurity.
f. False Positives and False Negatives
Despite its advanced capabilities, AI is not perfect. It can still produce false positives (flagging legitimate activities as threats) or false negatives (failing to detect actual threats). Both scenarios can undermine the effectiveness of cybersecurity measures and strain the resources of security teams.
g. Regulatory and Legal Challenges
As AI technology continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks and legal standards for its use in cybersecurity remain unclear in many regions. Organizations must navigate a complex landscape of compliance requirements while ensuring their AI systems align with legal and ethical guidelines.
h. Over-Reliance on AI
While AI enhances cybersecurity, over-relying on it can lead to complacency. Human oversight remains essential to ensure that AI systems are functioning as intended and to address scenarios where human judgment is necessary. Striking the right balance between automation and human involvement is crucial for effective cybersecurity.
5. Future of AI in Cybersecurity
The outlook for AI in cybersecurity is promising, with developments allowing for more proactive defense approaches such as real-time threat analysis and self-sufficient incident management. AI will improve predictive analytics to thwart attacks before they happen and will work alongside technologies like quantum computing for enhanced protection. Nevertheless, as AI progresses, cybercriminals might also take advantage of it, highlighting the importance for cybersecurity solutions to stay one step ahead in this swiftly evolving environment.
a. Advancements in Threat Intelligence
As AI technologies evolve, they are expected to enhance threat intelligence by providing even deeper insights into emerging cyber threats. AI-driven systems will likely integrate real-time data from diverse sources, such as dark web monitoring, social media, and global threat databases, to predict and counter new attack vectors before they materialize.
b. Wider Adoption of Autonomous Security Systems
In the future, fully autonomous cybersecurity systems powered by AI could become the norm. These systems will be capable of identifying, analyzing, and neutralizing threats without requiring human intervention. By operating around the clock with minimal downtime, autonomous systems will provide a robust line of defense for organizations of all sizes.
c. Enhanced Personalization of Security Measures
AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data will lead to more personalized security measures. For example, adaptive authentication methods could tailor security protocols to individual users based on their behavior and risk levels, offering an optimal balance between security and usability.
d. AI-Driven Collaboration
Future cybersecurity will benefit from collaborative AI systems that share insights across organizations and industries. These systems will create a unified network of defense, enabling faster responses to widespread threats and reducing the overall risk of large-scale cyberattacks.
e. Integration with Quantum Computing
As quantum computing becomes more accessible, its integration with AI could revolutionize cybersecurity. Quantum-powered AI systems will be capable of solving complex encryption and decryption challenges, strengthening defenses against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
f. Addressing AI Bias and Ethical Concerns
The future of AI in cybersecurity will also involve tackling inherent biases in algorithms and addressing ethical concerns surrounding data usage. Developing transparent and explainable AI systems will help build trust and ensure that cybersecurity solutions align with societal values and legal requirements.
g. Increased Focus on AI Regulation
With the growing use of AI in cybersecurity, governments and regulatory bodies are expected to establish clearer standards and guidelines for its deployment. These regulations will aim to ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly while safeguarding privacy and data integrity.
h. AI vs. AI: The Cybersecurity Arms Race
The ongoing battle between cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals will likely see both sides leveraging AI. As attackers develop more advanced AI tools to breach defenses, cybersecurity teams will need to innovate continuously to stay ahead. This dynamic will drive rapid advancements in AI capabilities and techniques.
6. Final Thought
AI has become a game-changer in the realm of cybersecurity, offering unprecedented capabilities to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. Its integration into key areas such as threat detection, user behavior analytics, automated incident response, and predictive analytics has enabled organizations to stay one step ahead of attackers.
However, alongside its many benefits, the implementation of AI in cybersecurity comes with challenges, including high costs, ethical considerations, and the need for human oversight. Addressing these obstacles will require ongoing innovation, collaboration, and regulatory clarity.
As we look to the future, AI’s role in cybersecurity will continue to expand, driving advancements in threat intelligence, autonomous systems, and personalized security measures. By leveraging AI responsibly and effectively, organizations can build stronger defenses against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Ultimately, while AI is not a silver bullet, it is an essential tool in the ongoing fight to protect digital assets and ensure the safety of our interconnected world. The integration of AI into cybersecurity is not just an option—it is a necessity for staying resilient in the face of growing cyber risks.















Leave a comment