In today’s digital world, where cyber threats lurk around every corner, protecting your network is not just important – it’s absolutely critical. Imagine your organization’s network as a busy city, with valuable information flowing like traffic. Without strong security, this city is open to all sorts of dangers, from sneaky thieves to organized crime. Cybersecurity, especially network security, acts as the police force, the border patrol, and the city planners all rolled into one, ensuring that only authorized traffic moves freely and that vital assets are protected. Let’s understand network security in cybersecurity.
Recent reports highlight the urgency: the average cost of a data breach reached a staggering $4.9 million in 2024, according to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report. This isn’t just about money; it’s about reputation, customer trust, and even the ability of a business to continue operating. For technical experts and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs), mastering network security is no longer an option but a core pillar of organizational resilience. It requires a proactive, multi-layered approach to defend against an ever-evolving landscape of cyberattacks.
Key Stats
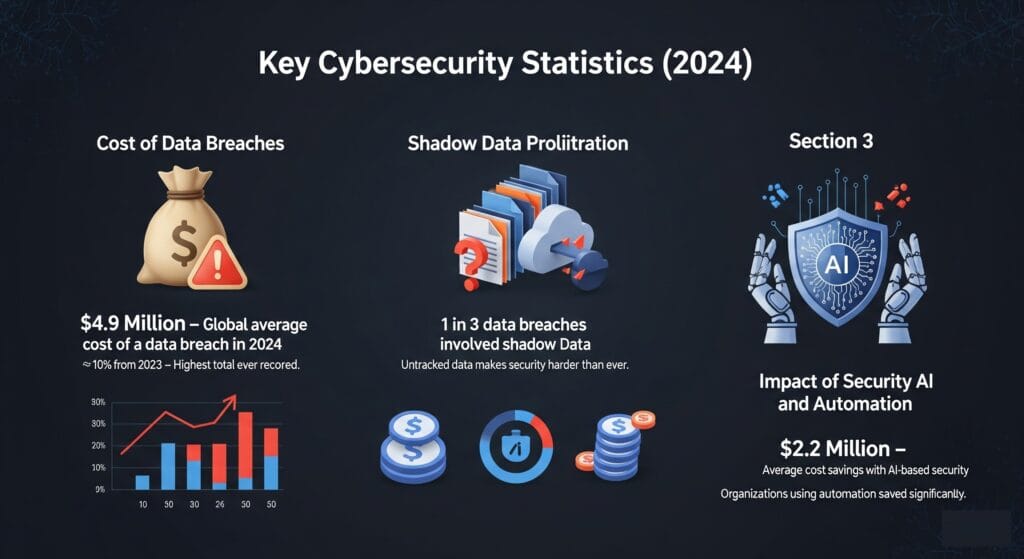
- Network security is vital for protecting digital assets and preventing costly data breaches, which averaged $4.9 million in 2024.
- Adopting a Zero Trust Architecture means “never trust, always verify” for all users and devices, significantly enhancing security.
- Advanced tools like SIEM, EDR, and XDR are crucial for detecting and responding to threats quickly using AI and machine learning.
- Strong access controls (MFA, least privilege) and network segmentation are key to limiting unauthorized access and containing breaches.
- Regular audits, employee training, and data encryption form a comprehensive defense, addressing both technical vulnerabilities and human factors.
The Foundation of Digital Defense:
What is Network Security in Cybersecurity: Top 7 Strategies
Network security refers to the strategies, tools, and processes designed to protect computer networks and data from unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial. It’s about building strong defenses around your digital infrastructure to keep cybercriminals out and sensitive information safe. Think of it as a comprehensive security system for your entire digital ecosystem, covering hardware, software, and data.
The landscape of cyber threats is constantly shifting. From sophisticated ransomware attacks that lock up your data and demand payment to subtle phishing schemes designed to steal credentials, attackers are always finding new ways to breach defenses. The rise of cloud computing, remote work, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has further expanded the attack surface, making network security more complex and critical than ever before. Organizations must understand the invisible threats posed by cybercrime to adequately protect themselves. Learn more about understanding cybercrime and the invisible threat.
To truly achieve excellence in network security, organizations must adopt a strategic, multi-faceted approach. Here are seven essential strategies that form the backbone of a robust cybersecurity posture.
1. Embrace Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
The traditional “castle-and-moat” security model, where everything inside the network is trusted, is no longer effective. Modern threats bypass perimeter defenses, making it essential to assume that breaches can and will occur. This is where Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) comes into play.
Zero Trust operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It means that every user, device, and application attempting to access network resources must be authenticated and authorized, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the traditional network perimeter.
Key Components of ZTA:
- Micro-segmentation: Breaking down the network into small, isolated zones, with strict security controls between them.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring more than one method of verification for user identity.
- Least Privilege Access: Granting users only the minimum access rights necessary to perform their job functions.
- Continuous Monitoring: Constantly monitoring all network traffic and activities for anomalies.
“Zero Trust isn’t just a technology; it’s a philosophy that fundamentally shifts how we approach security, moving from implicit trust to explicit verification for every access attempt.” – CTJ Expert
According to a 2022 report by the Cloud Security Alliance, 72% of organizations have either started or are planning to implement Zero Trust within the next 12-18 months. Implementing ZTA significantly reduces the risk of lateral movement by attackers once they gain initial access. For a deeper dive, explore Zero Trust Architecture.
2. Implement Advanced Threat Detection and Response
Detecting threats quickly and responding effectively is paramount. Traditional signature-based antivirus solutions are often insufficient against sophisticated, polymorphic malware and zero-day exploits. Modern network security relies on advanced tools that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to identify suspicious patterns and anomalies.
Key Technologies:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collects and analyzes security data from various sources across the network, providing a centralized view of security events. It helps identify potential threats and compliance issues.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Monitors endpoint devices (laptops, servers) for malicious activity, providing detailed insights and enabling rapid response.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Builds upon EDR by integrating security data from a wider range of sources, including networks, cloud environments, and email, offering a more holistic view of threats.
- Network Detection and Response (NDR): Focuses on network traffic analysis to detect suspicious behavior, even for encrypted communications.
The ability of AI to analyze vast amounts of data for subtle indicators of compromise (IOCs) is transforming threat detection. This is why the role of the CISO is evolving, with AI having a significant impact. Read more about AI’s impact on the CISO role in 2025. Furthermore, leveraging open-source threat detection tools can provide additional layers of defense and flexibility.
3. Fortify Access Control and Identity Management (IAM)
Who can access what, and under what conditions? These are fundamental questions addressed by robust Access Control and Identity Management (IAM) systems. Weak access controls are a common entry point for attackers.
Core Principles:
- Strong Authentication: Beyond simple passwords, implement MFA for all critical systems and accounts. This adds layers of security, making it much harder for attackers to gain access even if they steal credentials.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on a user’s role within the organization, ensuring they only have access to resources relevant to their job.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Specifically manages and monitors accounts with elevated privileges (e.g., administrator accounts), which are prime targets for attackers.
- Regular Access Reviews: Periodically review user access rights to ensure they are still appropriate and remove unnecessary permissions.
Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) consistently shows that compromised credentials remain a leading cause of data breaches. Strong IAM is your first line of defense against such attacks.
4. Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a computer network into smaller, isolated segments or subnets. This strategy limits the lateral movement of attackers within the network if a breach occurs in one segment.
Benefits of Segmentation:
- Containment: If one segment is compromised, the breach is contained, preventing it from spreading to the entire network.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Attackers have fewer targets to explore once inside.
- Improved Performance: Reduces network congestion.
- Enhanced Compliance: Easier to meet regulatory requirements by isolating sensitive data.
Types of Segmentation:
- VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks): Logical grouping of devices regardless of their physical location.
- Micro-segmentation: Even finer-grained segmentation, often down to individual workloads or applications, typically enforced by software-defined networking (SDN) or host-based firewalls.
Consider isolating critical servers, payment systems, and sensitive data repositories into their own segments. This makes it significantly harder for ransomware to spread or for attackers to reach high-value assets. Understanding how to encrypt sensitive files is also crucial in these segmented environments; learn more about how to encrypt sensitive files.
5. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Proactive identification of vulnerabilities is far more effective than reactive incident response. Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential for uncovering weaknesses before attackers exploit them.
- Security Audits: Comprehensive reviews of an organization’s security posture, policies, and controls. They assess compliance with standards (e.g., NIST, ISO 27001) and identify gaps.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Use automated tools to scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing (Pen Testing): Ethical hackers simulate real-world attacks to find exploitable weaknesses in networks, applications, and systems. This provides a realistic view of an organization’s resilience against actual threats.
“If you don’t test your defenses, you don’t know how strong they are. Penetration testing is a crucial reality check.” – CTJ
Regular testing helps organizations understand their current security posture, prioritize remediation efforts, and measure improvement over time. This also ties into the need for a robust disaster recovery plan. Ensure you know how to prepare a disaster recovery plan for your business.
6. Prioritize Employee Training and Awareness
Technology alone cannot secure a network. The human element is often the weakest link in the security chain. Employees can inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities through phishing attacks, weak password practices, or succumbing to social engineering tactics.
Key Training Areas:
- Phishing Awareness: Training employees to recognize and report phishing emails, which are a primary vector for initial network breaches.
- Password Best Practices: Educating on creating strong, unique passwords and using password managers.
- Social Engineering: Teaching employees to identify and resist attempts by attackers to manipulate them into divulging sensitive information.
- Data Handling: Guidelines for securely handling sensitive data, whether in transit or at rest.
- Incident Reporting: Empowering employees to know when and how to report suspicious activity.
Regular, engaging security awareness training can significantly reduce the risk of human error-induced breaches. A well-informed workforce acts as an additional layer of defense.
7. Implement Robust Data Encryption and DLP
Data is the ultimate target for cybercriminals. Protecting data, both when it’s stored (at rest) and when it’s moving across networks (in transit), is non-negotiable.
Data Encryption:
- Data at Rest: Encrypting databases, hard drives, and cloud storage ensures that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable without the decryption key.
- Data in Transit: Using protocols like SSL/TLS (for web traffic) and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) encrypts data as it travels across networks, protecting it from eavesdropping. Understanding certificates and their global role is fundamental to secure data in transit.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor, detect, and block sensitive data from leaving the corporate network, whether accidentally or maliciously. This includes preventing data from being emailed outside the organization, uploaded to unauthorized cloud services, or copied to USB drives.
According to a report by Statista, 76% of organizations consider encryption to be a critical component of their overall security strategy. Implementing strong encryption practices is fundamental to protecting intellectual property, customer data, and regulatory compliance.
The Future of Network Security: Quantum and Beyond
As technology advances, so do the threats. The emergence of quantum computing, while still in its early stages, poses a future threat to current encryption methods. This is why quantum cybersecurity is the new battleground in the race between hackers and cybersecurity professionals. Organizations must stay informed about these future challenges and begin to consider post-quantum cryptography.
Moreover, the increasing sophistication of ransomware attacks requires continuous vigilance and robust incident response plans. Knowing how to remove ransomware is a critical skill for any security team. Even secure communication apps can be targeted; understanding the security of encrypted apps amid cyberattacks in 2025 will become increasingly vital.
Assess Your Network Security Posture
Use the following interactive checklist to get a quick assessment of your organization’s current network security posture based on the strategies discussed.
Network Security Self-Assessment Checklist 🛡️
Answer ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ to assess your organization’s security posture across key strategies.
Building a Resilient Defense
Mastering network security is an ongoing journey, not a destination. The digital threat landscape is constantly evolving, requiring organizations to be agile, proactive, and committed to continuous improvement. By strategically implementing Zero Trust, advanced threat detection, robust access controls, network segmentation, regular auditing, comprehensive employee training, and strong data encryption, organizations can build a formidable defense against cyber threats.
For CISOs and technical experts, the challenge lies not just in adopting these technologies but in integrating them into a holistic, resilient security framework that protects critical assets and ensures business continuity. Investing in these strategies today is an investment in the future resilience and success of your organization.














Leave a comment