In 2025, the digital world is more connected and advanced than ever before. While this brings many benefits, it also opens new doors for cybercriminals. One of the biggest dangers emerging right now is generative AI cyber fraud. This isn’t just about simple email scams anymore. We’re talking about incredibly realistic, AI-driven scams that can mimic voices, create fake videos, and write convincing messages, making it harder than ever for businesses to tell what’s real and what’s fake.
Imagine a scammer calling your finance department, sounding exactly like your CEO, asking for an urgent money transfer. Or an email appearing to be from a trusted supplier, with perfect grammar and details, asking you to update payment information to a fraudulent account. These are the kinds of sophisticated threats that generative AI brings to the table, making GenAI cybersecurity risks a top concern for every business in 2025. This article will explore these threats and provide essential strategies to protect your business.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Generative AI cyber fraud uses advanced AI to create highly realistic scams, like deepfake videos and voice cloning, making traditional defenses less effective.
- AI-driven scams are becoming incredibly personalized and convincing, targeting businesses with sophisticated phishing, social engineering, and business email compromise (BEC) attacks.
- Deepfake phishing attacks leverage AI to mimic real people’s voices and appearances, tricking employees into giving up sensitive information or transferring funds.
- Businesses face significant GenAI cybersecurity risks, including financial loss, reputational damage, and data breaches, requiring updated security strategies.
- Effective protection involves strong employee training, advanced detection tools, multi-factor authentication, and robust cyber hygiene practices in 2025.
What is Generative AI Cyber Fraud?
Generative AI (GenAI) refers to artificial intelligence systems that can create new content, such as text, images, audio, and video, that is often indistinguishable from content created by humans. Think of tools like ChatGPT for text, Midjourney for images, or advanced voice synthesizers. While these technologies have many positive uses, they also provide powerful new tools for cybercriminals.
When we talk about generative AI cyber fraud, we’re referring to the malicious use of these AI capabilities to commit fraud. This can involve:
- Creating realistic fake identities: AI can generate convincing profile pictures and backstory details for fake social media accounts or fake employees.
- Crafting highly personalized phishing emails: GenAI can write emails that perfectly mimic a specific person’s writing style or a company’s typical communication, making them much harder to spot than older, generic phishing attempts.
- Generating deepfake audio and video: This is perhaps the most alarming aspect. AI can clone someone’s voice or create a video of them saying things they never said, leading to incredibly convincing scams.
The core problem is that GenAI lowers the barrier for creating sophisticated scams. Even criminals with limited technical skills can now access tools that produce high-quality, deceptive content. This means more frequent, more convincing, and more targeted attacks against businesses.
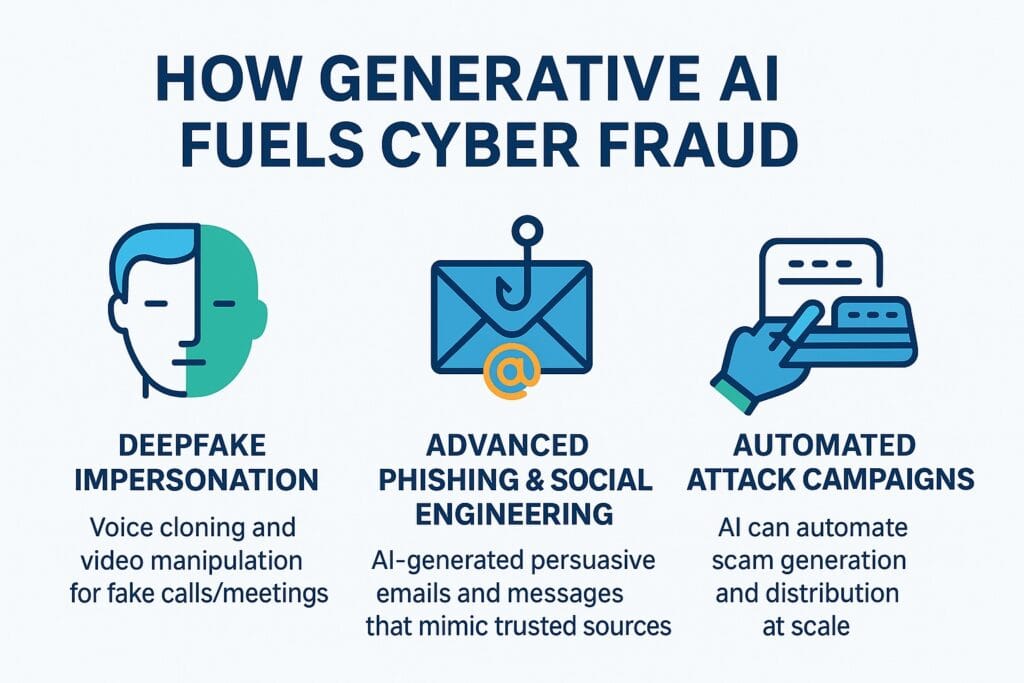
The Rise of AI-Driven Scams: New Threats for 2025
The year 2025 marks a turning point in cybersecurity. The adoption of generative AI by cybercriminals is no longer theoretical; it’s a reality. Businesses are now facing an onslaught of AI-driven scams that are far more sophisticated than anything seen before.
- Personalized Phishing at Scale: AI can analyze publicly available information about employees and companies to craft highly personalized phishing emails. Instead of generic “Your account has been suspended” emails, you might receive one referencing a recent company event, a specific project, or even a personal interest, making it incredibly convincing.
- AI-Powered Social Engineering: Social engineering relies on tricking people into breaking security rules or giving up information. AI excels at this by creating believable stories, urgent requests, and emotional appeals. It can automate conversations, making a chatbot seem like a real person, slowly extracting sensitive data over time. This kind of AI-powered social engineering is a major concern.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) on Steroids: BEC attacks, where scammers impersonate executives or vendors to trick employees into making fraudulent payments, are already costly. With generative AI, these attacks become even more potent. AI can learn the writing style of an executive, making fake emails virtually indistinguishable from real ones.
In 2025, the human element remains the weakest link, but generative AI is making that link even easier for attackers to exploit with hyper-realistic deception.
Deepfake Phishing Attacks: Seeing Isn’t Always Believing
Perhaps the most alarming development in generative AI cyber fraud is the rise of deepfake technology. Deepfakes use AI to create highly realistic fake videos or audio recordings. For businesses, this means new and dangerous forms of phishing:
- Voice Cloning Scams: Imagine getting a phone call from what sounds exactly like your CEO, asking you to urgently transfer funds to a new account for a secret acquisition. Thanks to AI voice cloning, this scenario is no longer science fiction. Criminals can use short audio clips of a person’s voice (easily found online) to train AI models that can then generate new speech in that person’s voice.
- Deepfake Video Conferences: As remote work continues to be common, video calls are standard. Attackers could potentially use deepfake video to impersonate an executive or a partner in a video conference, instructing employees to take fraudulent actions. While still complex, the technology is advancing rapidly.
- Targeted Whaling Attacks: Deepfakes elevate “whaling” attacks (phishing targeting high-level executives) to a new level. An attacker could impersonate a board member or a major client, creating a sense of urgency and authority that bypasses typical skepticism.
These deepfake phishing attacks are incredibly difficult to detect with the naked eye or ear, putting immense pressure on employees and security systems to verify identities and requests through other means.
AI-Powered Social Engineering: The Art of Digital Deception
Social engineering is a timeless tactic for criminals, but generative AI has given it a massive upgrade. AI-powered social engineering makes it easier than ever for attackers to manipulate individuals into performing actions or divulging confidential information.
Here’s how AI enhances these attacks:
- Contextual Awareness: AI can quickly process vast amounts of data from social media, news articles, and company websites to build a detailed profile of a target. This allows scammers to tailor their approach with highly specific and relevant details, making their stories much more believable.
- Emotional Manipulation: GenAI models can be trained to understand and exploit human emotions. They can craft messages designed to evoke fear, urgency, curiosity, or sympathy, pushing targets to react quickly without critical thought.
- Multi-channel Attacks: AI can coordinate attacks across multiple platforms. For example, a scam might start with a convincing email, followed by a personalized text message, and then a social media interaction, all designed to build trust and pressure the victim. This is especially dangerous when considering the prevalence of WhatsApp and SMS scams that can now be generated with AI-perfected language.
The sheer volume and sophistication of these attacks mean that businesses must go beyond basic awareness training. Employees need to be educated on the subtle signs of AI-enhanced deception.
GenAI Cybersecurity Risks for Businesses: What’s at Stake?
The threats posed by generative AI cyber fraud translate into significant GenAI cybersecurity risks for businesses of all sizes in 2025. The potential consequences are severe:
- Financial Loss: Direct loss of funds through fraudulent transfers, payments to fake vendors, or ransomware attacks facilitated by AI-driven access.
- Data Breaches: AI can be used to craft more effective credential phishing, leading to stolen login details and subsequent access to sensitive customer data, intellectual property, or financial records.
- Reputational Damage: A high-profile scam or data breach can severely damage a company’s reputation, eroding customer trust and impacting future business.
- Operational Disruption: If critical systems are compromised, operations can come to a standstill, leading to significant downtime and recovery costs.
- Legal and Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with data protection regulations (like GDPR or CCPA) following a breach can result in hefty fines.
The stakes are incredibly high, making proactive defense against these new threats absolutely essential for business continuity and success in 2025.
Protecting Your Business from Generative AI Threats: Strategies for 2025
Combating generative AI cyber fraud requires a multi-layered and adaptive approach. Here are key strategies businesses should implement in 2025:
1. Enhance Employee Training and Awareness
Your employees are your first line of defense.
- Regular, Realistic Training: Move beyond generic phishing tests. Conduct training that includes examples of AI-generated content, deepfake audio, and sophisticated social engineering tactics.
- “Verify, Don’t Trust” Culture: Emphasize the importance of verifying any unusual or urgent requests, especially those involving financial transfers or sensitive information, through an independent channel (e.g., calling the sender back on a known number, not the one provided in the email).
- Spotting the Subtle Signs: Train employees to look for inconsistencies, even minor ones, in grammar, tone, or visual cues that might indicate AI-generated content.
2. Implement Advanced Detection and Prevention Tools
Traditional security tools may not be enough.
- AI-Powered Security Solutions: Invest in cybersecurity tools that use AI themselves to detect anomalous behavior, identify deepfakes, and flag suspicious communications. Look for solutions capable of shadow AI detection, which can identify unauthorized or risky AI usage within your organization.
- Email Security Gateways (ESG): Ensure your ESG is up-to-date and uses advanced threat protection, including AI-driven anomaly detection, to filter out sophisticated phishing attempts.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions can monitor endpoints for malicious activity that might result from a successful social engineering attack.
3. Strengthen Identity Verification and Access Controls
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA everywhere possible. Even if credentials are stolen through an AI-driven phishing attack, MFA acts as a crucial second barrier.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant employees only the minimum access necessary for their roles to limit the damage if an account is compromised.
- Regular Access Reviews: Periodically review who has access to what, ensuring that privileges are appropriate and up-to-date.
4. Practice Robust Cyber Hygiene
Good basic security practices are more critical than ever.
- Patch Management: Keep all software and systems updated to patch known vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce complex, unique passwords, ideally managed through a password manager.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up critical data and test your recovery plans. This is a core component of overall cyber hygiene in 2025.
5. Develop and Test an Incident Response Plan
Knowing what to do when an attack occurs can significantly reduce its impact.
- Clear Protocols: Establish clear procedures for reporting suspicious activity, verifying requests, and responding to confirmed incidents.
- Regular Drills: Conduct simulated cyberattacks, including those involving AI-driven scenarios, to test your team’s readiness and identify weaknesses.
- Focus on Resilience: Build cyber resilience into your operations, especially for critical infrastructure. Learn more about ICS cyber resilience and building business continuity beyond firewalls and best practices for cybersecurity in industrial control systems in 2025.
The Future of Generative AI and Cybersecurity
The battle against generative AI cyber fraud is an ongoing one. As AI technology advances, so too will the tactics of cybercriminals. Businesses must remain agile, continuously updating their defenses and educating their workforce.
Looking ahead, we can expect:
- More Sophisticated AI-driven Scams: Attacks will become even more convincing, personalized, and harder to detect.
- AI vs. AI: Cybersecurity solutions will increasingly rely on AI to detect and counter AI-generated threats, creating an arms race between attackers and defenders.
- Greater Emphasis on Verification: Trust will become a scarce commodity, making independent verification processes even more critical for all digital interactions.
- New Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and industry bodies may introduce new regulations specifically addressing the misuse of generative AI.
The threats posed by AI are serious, but with the right strategies and a proactive mindset, businesses can build robust defenses. Staying informed about the latest threats, like evolving WhatsApp and SMS scams that leverage GenAI, is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture.
Bottom Line
Generative AI cyber fraud presents an unprecedented challenge for businesses in 2025. The ability of AI to create hyper-realistic deepfakes, sophisticated phishing emails, and convincing social engineering tactics means that traditional security measures are no longer enough. By understanding these AI-driven scams and implementing a comprehensive defense strategy—including advanced employee training, cutting-edge security tools, strong identity verification, robust cyber hygiene, and a well-tested incident response plan—businesses can significantly reduce their GenAI cybersecurity risks. The future of business security hinges on our ability to adapt and protect against these intelligent, evolving threats.













Leave a comment