Have you ever stopped to think about all the information your business collects, uses, and stores every single day? From customer names and addresses to financial records and secret project plans, data is the lifeblood of modern organizations. But just like any valuable asset, it needs serious protection. Imagine leaving your front door wide open with all your valuables on display – that’s what it’s like to operate without a solid data protection strategy.
In today’s digital age, data breaches are unfortunately common, and the rules about how we handle personal information are getting stricter. This isn’t just a technical problem for your IT team; it’s a core business challenge that affects everything from your reputation to your bottom line. That’s why building a strong data protection strategy isn’t just a good idea – it’s absolutely essential. It’s about more than just putting up a firewall; it’s about understanding what data you have, who can access it, and how you keep it safe throughout its entire journey.
Table of Contents
I’m here to walk you through the key pillars of a robust data protection strategy: understanding your data through classification, setting the rules with governance, and putting strong safeguards in place with privacy controls. Let’s dive in and learn how to keep your valuable information safe and sound.
Key Summary
- Know Your Data: Begin by classifying your data based on its sensitivity and importance. This helps you understand what needs the most protection.
- Set the Rules: Establish clear data governance policies that define who is responsible for data, how it’s handled, and what rules apply to its use and storage.
- Protect Privacy: Implement strong privacy controls, including technical safeguards like encryption and access limits, and administrative measures like employee training, to protect sensitive information.
- Plan and Adapt: A strong data protection strategy is an ongoing process that requires regular assessment, clear policies, proper technology, and continuous employee training. It’s not a one-time fix!
Why a Data Protection Strategy Matters More Than Ever
Think about it: every day, new threats emerge. Cybercriminals are always looking for weaknesses, and even honest mistakes can lead to big problems. Plus, governments around the world are passing strict laws like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California to make sure companies protect people’s personal information. If you don’t follow these rules, you could face huge fines and lose your customers’ trust.
A well-thought-out data protection strategy isn’t just about avoiding trouble; it’s about building trust. When your customers know their information is safe with you, they’re more likely to do business with you. It also helps your team work more efficiently because everyone knows the rules for handling data. In short, it’s about being responsible and smart in how you manage your most valuable digital assets.
In the digital age, data is the new gold, and a robust data protection strategy is your unbreachable vault.
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, it’s important to understand that data protection is a big part of overall information security. If you’re curious about the broader picture, you can learn more about understanding information security and its role in cybersecurity. It’s all connected!
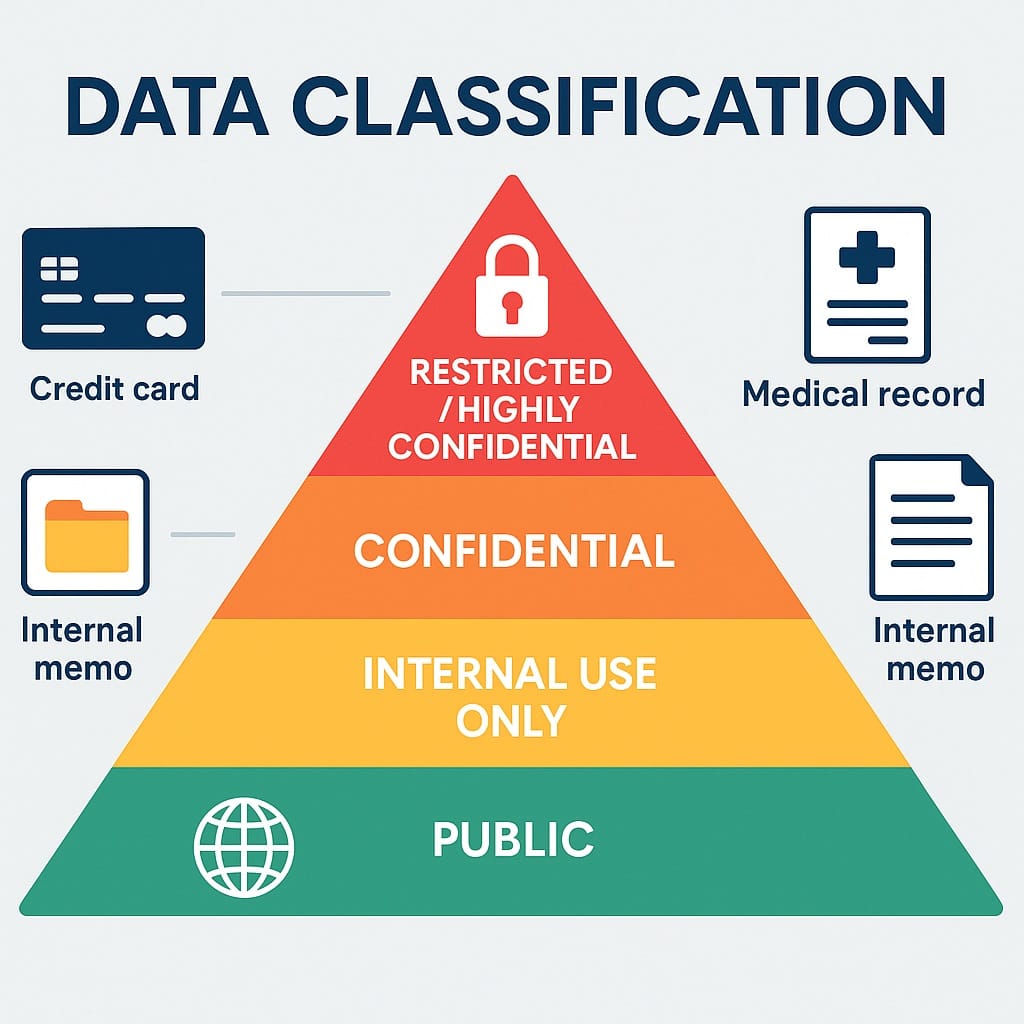
Pillar 1: Data Classification – Knowing What You’ve Got
Imagine you have a huge closet full of clothes. If everything is just thrown in randomly, it’s impossible to find what you need quickly, and you might accidentally damage your most expensive items. Data is similar. If you don’t know what kind of data you have, where it is, or how sensitive it is, how can you protect it properly? That’s where data classification comes in.
What is Data Classification?
Data classification is like organizing your digital closet. It’s the process of categorizing data based on its sensitivity, value, and the impact if it were to be lost, stolen, or misused. This helps you apply the right level of protection to the right data. You wouldn’t put the same lock on a shed as you would on a bank vault, right? The same goes for data.
Why is Data Classification So Important?
- Right-Sized Security: It helps you apply appropriate security measures. Highly sensitive data gets top-tier protection, while less sensitive data might have standard safeguards. This saves resources and makes your security efforts more effective.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many data privacy laws require you to know what kind of personal data you’re collecting and how you’re protecting it. Classification is the first step to meeting these requirements.
- Risk Management: By identifying your most critical data, you can better understand your risks and focus your efforts on protecting what matters most.
- Improved Efficiency: When data is properly classified, it’s easier to find, manage, and share securely with authorized individuals.
How Do We Classify Data?
Typically, organizations use different levels or categories for data classification. While the exact names might vary, here are common examples:
Public Data: Information that can be freely shared with anyone without causing harm to the organization or individuals.
- Examples: Company website content, press releases, marketing materials.
- Protection Level: Minimal.
Internal Use Only Data: Information not meant for public consumption but doesn’t contain highly sensitive details. Its disclosure might cause minor inconvenience or competitive disadvantage.
- Examples: Internal memos, non-sensitive company policies, general project plans.
- Protection Level: Standard access controls, internal sharing restrictions.
Confidential Data: Information that, if disclosed, could cause significant harm to the organization, its employees, or its customers. This often includes proprietary business information.
- Examples: Business strategies, financial reports, employee records (non-PII), intellectual property.
- Protection Level: Strong access controls, encryption, need-to-know basis.
Restricted/Highly Confidential Data: The most sensitive data, often containing personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), or financial data. Unauthorized disclosure could lead to severe legal penalties, financial loss, or reputational damage.
- Examples: Customer credit card numbers, social security numbers, medical records, trade secrets.
- Protection Level: Highest level of security, including multi-factor authentication, strong encryption, strict access logging, and regular audits.
Steps to Implement Data Classification
- Identify Data Owners: Determine who is responsible for different types of data within your organization.
- Define Classification Levels: Create clear, easy-to-understand categories for your data, similar to the examples above.
- Inventory Your Data: Find out where all your data resides – on servers, laptops, cloud storage, external drives, etc.
- Tag and Label Data: Apply the classification labels to your data. This can be done manually or with automated tools.
- Develop Policies: Create rules about how each classification level should be handled, stored, and accessed.
- Train Employees: Make sure everyone understands the classification levels and their responsibilities. This is crucial because human error is a common cause of data breaches.
Pillar 2: Data Governance – Who’s in Charge and How?
Once you know what data you have (classification), the next step is to set up the rules for how that data is managed throughout its entire life. This is where data governance comes in. Think of it as the steering wheel and rulebook for your data. Without it, even classified data can become a mess, leading to inconsistencies, errors, and security gaps.
What is Data Governance?
Data governance is a set of rules, processes, and responsibilities that ensures data is managed consistently, accurately, securely, and in compliance with regulations. It answers questions like:
- Who owns this data?
- Who can access it?
- How long should we keep it?
- What happens to it when we no longer need it?
- How do we ensure its quality and accuracy?
It’s not just about security; it’s about the overall health and reliability of your data. For businesses, understanding cybersecurity for businesses: the ultimate guide to protecting your company can provide a broader context for how data governance fits into your overall security posture.
Key Components of Data Governance
A strong data governance framework includes several critical elements:
- Data Policies and Standards: These are the written rules that define how data should be collected, stored, used, shared, and destroyed. They cover everything from data quality to security.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define who is accountable for data at different stages. This includes data owners, data stewards, and data custodians.
- Data Owners: High-level individuals (e.g., department heads) responsible for the strategic value and protection of specific data sets.
- Data Quality Management: Processes to ensure data is accurate, complete, consistent, and timely. Bad data can lead to bad decisions!
- Data Lifecycle Management: Managing data from its creation to its eventual disposal. This includes:
- Creation/Collection: How data is initially gathered.
- Storage: Where and how data is stored (on-premises, cloud).
- Usage: How data is accessed and used by authorized personnel.
- Sharing/Transfer: Rules for sharing data internally and externally (e.g., with third-party vendors). This is where understanding third-party risk assessment becomes vital.
- Archiving: Moving old but still necessary data to long-term storage.
- Destruction: Securely deleting data when it’s no longer needed or legally required.
- Compliance and Audit: Regularly checking that data policies are being followed and that the organization is meeting regulatory requirements.
The Importance of a Data Governance Framework
Without clear governance, your data can quickly become a wild west. Different departments might have their own ways of doing things, leading to inconsistencies and security gaps. A formal framework ensures everyone is on the same page, reducing risks and improving data’s overall usefulness.
Think about the recent ICBC Bank ransomware attack. While the specifics of their data governance aren’t public, such incidents often highlight weaknesses in data management, including how data is protected, backed up, and recovered. Strong governance helps prevent and recover from such disasters.
Pillar 3: Privacy Controls – Protecting Personal Information
Even with data classified and strong governance in place, you still need specific safeguards to protect the data itself, especially personal and sensitive information. These are your privacy controls. They are the technical, administrative, and physical measures designed to prevent unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of data.
What Are Privacy Controls?
Privacy controls are the mechanisms you put in place to enforce your data protection policies and governance rules. They ensure that data privacy is maintained. They are your security measures in action!
Types of Privacy Controls
- Technical Controls: These are the technology-based safeguards that protect data.
- Encryption: Converting data into a coded form to prevent unauthorized access. If someone steals encrypted data, they can’t read it without the decryption key. This is essential for data at rest (stored) and data in transit (moving across networks).
- Access Controls: Limiting who can access specific data based on their role and need. This includes:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Users are granted access based on their job function. A marketing person doesn’t need access to HR records, for example.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring more than one way to prove identity (e.g., password + a code from your phone).
- Principle of Least Privilege: Users should only have the minimum access necessary to do their job.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Tools that monitor, detect, and block sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, whether accidentally or maliciously.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDPS): Tools that monitor network traffic and block suspicious activity.
- Regular Backups: Creating copies of data to restore it in case of loss or corruption.
- Security Patches and Updates: Keeping all software and systems up-to-date to fix known vulnerabilities. Even a single unpatched vulnerability, like CVE-2024-55591 Fortinet Zero-Day Vulnerability, can be a huge risk.
- Pseudonymization and Anonymization: Techniques to make it harder to identify individuals from data, especially for analytical purposes. Pseudonymization replaces identifying information with artificial identifiers, while anonymization makes identification impossible.
- Administrative Controls: These are the policies, procedures, and training programs that guide human behavior and organizational processes.
- Security Policies: Formal documents outlining rules for data handling, acceptable use, incident response, etc.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educating employees about data protection best practices, recognizing threats (like fake job offers scams or phishing), and their role in protecting data. This is perhaps one of the most critical controls, as people are often the weakest link.
- Incident Response Plan: A detailed plan for how to react if a data breach or security incident occurs. Who does what, when, and how?
- Vendor Management: Assessing and managing the data security practices of third-party vendors who handle your data. Again, understanding third-party risk assessment is key here.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Periodically reviewing your data protection measures to ensure they are effective and compliant.
- Physical Controls: Safeguards that protect physical access to data storage facilities and equipment.
- Locked Doors and Access Cards: Limiting who can enter server rooms or data centers.
- Surveillance Cameras: Monitoring physical spaces where data is stored.
- Environmental Controls: Maintaining proper temperature and humidity to protect hardware.
Compliance with Regulations
Implementing strong privacy controls is crucial for complying with various data privacy regulations. Laws like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and others mandate specific controls and require organizations to demonstrate how they protect personal data. Failing to do so can lead to severe penalties and reputational damage. For example, consider the dangers of social media privacy invasion – strong privacy controls prevent your organization from contributing to such issues.
Building Your Data Protection Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we’ve covered the three pillars, let’s look at how to put it all together into a comprehensive data protection strategy. It’s not a one-time project; it’s an ongoing journey.
Step 1: Assess Your Current State
Before you can build, you need to know what you’re starting with.
- Data Inventory: What data do you have? Where is it stored? Who uses it?
- Risk Assessment: What are the biggest threats to your data? What are your vulnerabilities?
- Compliance Check: Are you currently meeting all relevant data protection laws and regulations?
- Existing Controls Review: What security measures do you already have in place? Are they effective?
Step 2: Define Your Goals and Scope
What do you want to achieve with your data protection strategy?
- Business Objectives: How does data protection support your overall business goals?
- Compliance Requirements: What specific regulations must you comply with?
- Risk Tolerance: How much risk are you willing to accept?
- Scope: Will this strategy cover all data, specific departments, or certain systems? Start small if you need to, then expand.
Step 3: Develop Policies and Procedures
This is where you formalize your data governance rules and privacy controls.
- Data Classification Policy: Define your classification levels and how data will be labeled.
- Access Control Policy: Who can access what data, and under what conditions?
- Data Retention Policy: How long different types of data should be kept.
- Incident Response Plan: A detailed guide for handling data breaches.
- Vendor Security Policy: Rules for third parties handling your data.
- Employee Acceptable Use Policy: Guidelines for how employees should handle company data.
Step 4: Implement Technology and Tools
Once policies are defined, choose and deploy the right technologies to support them.
- Data Discovery & Classification Tools: Software to help find and tag data.
- Encryption Solutions: For data at rest and in transit.
- Access Management Systems: To enforce role-based access and MFA.
- DLP Solutions: To prevent data from leaving your control.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: To monitor security events and identify threats.
- Backup and Recovery Solutions: To ensure business continuity.
Step 5: Train Your Team and Foster a Culture of Security
Technology alone isn’t enough. Your people are your first line of defense.
- Regular Training: Educate all employees on data protection policies, common threats, and their responsibilities. Make it engaging!
- Awareness Campaigns: Keep data protection top of mind with reminders, posters, and internal communications.
- Leadership Buy-in: Ensure management supports and champions the data protection strategy.
- Empower Data Stewards: Give those responsible for data governance the authority and resources they need.
- For those considering a career in this field, it’s worth exploring is cybersecurity for anyone entering the digital defense frontier in 2025? – because everyone plays a role.
Step 6: Monitor, Review, and Adapt
The digital landscape is constantly changing, so your strategy must evolve.
- Regular Audits: Periodically check if your controls are effective and if you’re still compliant.
- Performance Metrics: Track key indicators like the number of security incidents, compliance rates, and training completion.
- Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about new cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
- Policy Updates: Review and update your policies regularly to reflect new technologies, threats, and regulations.
- Incident Review: Learn from any incidents that occur and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Building a robust data protection strategy isn’t without its hurdles. Here are a few common ones and how to tackle them:
- Resistance to Change: People naturally resist new rules or processes.
- Solution: Communicate the “why” clearly. Explain the benefits (reduced risk, better reputation) and involve employees in the process. Make training engaging and easy to understand.
- Budget Constraints: Data protection requires investment in technology and personnel.
- Solution: Focus on risk. Prioritize protecting your most critical data first. Demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) by showing the potential costs of a breach versus the cost of prevention.
- Complexity of Data Environments: Modern businesses often have data spread across many systems, clouds, and devices.
- Solution: Start with a phased approach. Focus on critical systems first. Leverage automation tools for data discovery and classification where possible.
- Lack of Expertise: Finding skilled cybersecurity and data privacy professionals can be tough.
- Solution: Invest in training existing staff, consider external consultants, or look into managed security services. Remember, the role of a CISO is evolving, and AI’s impact on the CISO role in 2025 highlights the need for continuous learning.
- Maintaining Compliance: Regulations are complex and constantly changing.
- Solution: Dedicate resources to staying updated on compliance requirements. Use governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) software to help manage obligations.
The Future of Data Protection
Data protection is an ever-evolving field. As technology advances, so do the threats. We’re seeing more use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in both attacking and defending data. Automation will play a bigger role in identifying risks and enforcing policies. Data privacy will continue to be a hot topic, with more countries implementing stricter laws.
For industries like aerospace, a strong aerospace cybersecurity strategy is becoming non-negotiable due to the highly sensitive data involved. This trend of tailored, industry-specific data protection will only grow.
The core principles of classification, governance, and controls will remain, but the tools and techniques we use will become more sophisticated. The goal will always be the same: to keep our valuable digital assets safe and build trust in our digital world.
Your Data, Your Responsibility
Building a robust data protection strategy is not just a checkbox exercise; it’s a fundamental part of running a responsible and successful business in the 21st century. By systematically classifying your data, establishing clear governance rules, and implementing strong privacy controls, you’re not just protecting information – you’re safeguarding your reputation, ensuring compliance, and building lasting trust with your customers and partners.
It’s an ongoing commitment, requiring continuous effort, vigilance, and adaptation. But the peace of mind, reduced risk, and strengthened business foundation that come with a well-executed data protection strategy are invaluable. So, take these steps, empower your team, and make data protection a core part of your organization’s DNA. Your digital future depends on it!















Leave a comment