Imagine a world where air travel isn’t safe. Sounds scary, right? The aerospace industry, which includes everything from airplanes and airports to air traffic control systems, is a vital part of our modern world. It connects people, moves goods, and plays a huge role in global economies. But just like any other important system, it faces serious dangers from cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity in aerospace isn’t just about keeping computers safe; it’s about protecting lives, national security, and critical infrastructure. A strong aerospace cybersecurity strategy is absolutely essential to keep our skies secure and our travel safe.
Key Insides
- High Stakes, High Risk: The aerospace industry is a top target for cyberattacks because any disruption can have huge impacts on safety, economy, and national security.
- Unique Challenges: Protecting aviation systems is tough due to old and new technologies working together, complex global networks, and the need for constant operation.
- Core Strategy Pillars: A good strategy includes managing risks, watching for threats, controlling who accesses systems, building secure software, and having a plan for when attacks happen.
- People and Rules Matter: Training staff and following strict regulations are just as important as technology in building strong cyber defenses.
- Future-Proofing is Key: Staying ahead of new threats like AI-powered attacks and quantum computing challenges requires ongoing learning, new tech, and teamwork across the industry.
Why Aerospace is a Prime Target
The aerospace industry is a shining beacon of human innovation, but its very importance makes it a magnet for cybercriminals, spies, and even terrorists. Why?
- High Value Targets: Airlines, aircraft manufacturers, and defense contractors handle incredibly valuable data, including intellectual property (like new plane designs), passenger information, and sensitive military secrets.
- Massive Impact: A successful cyberattack could cause:
- Safety Risks: Imagine flight control systems being messed with! ✈️ This could lead to accidents or serious delays.
- Economic Chaos: Grounding flights or disrupting supply chains costs billions.
- National Security Threats: If military aircraft or defense systems are compromised, it could put entire nations at risk.
- Loss of Trust: People wouldn’t feel safe flying if they knew systems were vulnerable.
Unique Cybersecurity Challenges in Aviation
Protecting the aerospace sector isn’t like protecting a regular office network. It comes with its own set of very specific and tough challenges:
- Legacy Systems: Many older aircraft and ground systems still rely on technology designed before modern cyber threats even existed. Updating these “legacy” systems is complex and expensive.
- Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) Blending: Unlike many industries, aerospace heavily relies on operational technology (OT) – the systems that control physical processes, like flight controls and navigation. These are now increasingly connected to IT networks, creating new pathways for attackers.
- Global Interconnectedness: Airlines operate worldwide, linking many different countries, systems, and partners. This creates a vast, complex network that’s hard to secure end-to-end.
- Long Lifecycles: Airplanes are built to last decades. This means the cybersecurity measures put in place today must protect against threats that haven’t even been invented yet!
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: A single aircraft or system involves thousands of parts and software components from various suppliers. A weakness in just one part of this huge supply chain can open doors for attackers.
In aerospace, a cyberattack isn’t just a data breach; it’s a potential safety hazard. The stakes couldn’t be higher.
Core Pillars of an Aerospace Cybersecurity Strategy
Building a strong aerospace cybersecurity strategy requires a multi-layered approach. It’s like building a fortress with many walls, guards, and alarm systems. Here are the key pillars:
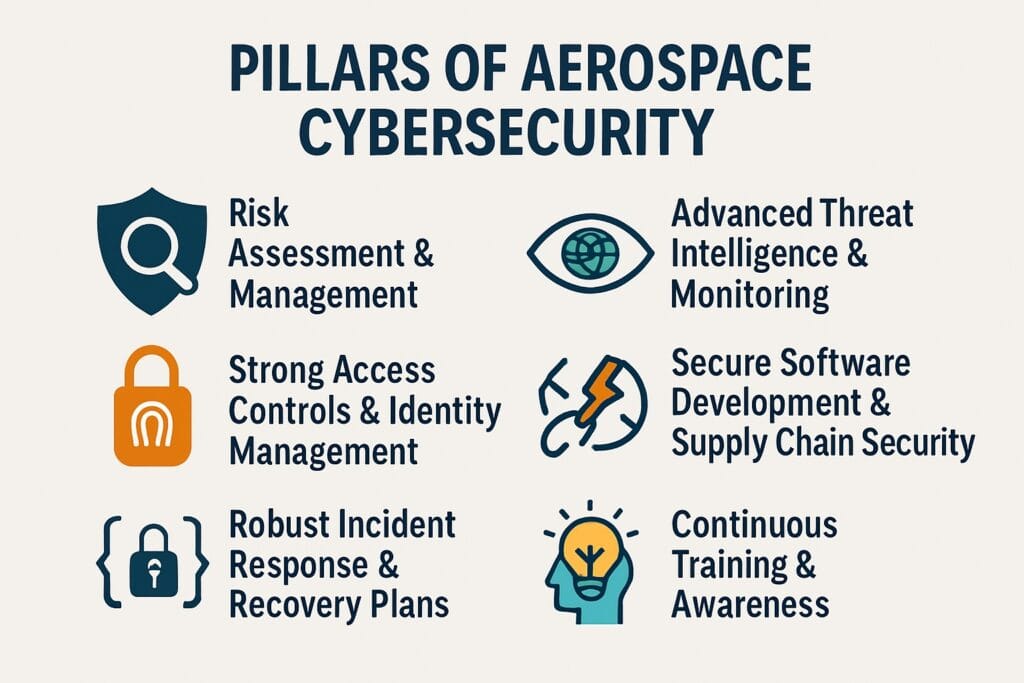
1. Robust Risk Assessment & Management
Before you can protect something, you need to know what you’re protecting and what threats it faces.
- Identify Assets: What are the most important systems, data, and operations? (e.g., flight control, air traffic communication, passenger data).
- Assess Vulnerabilities: Where are the weaknesses? This could be old software, unpatched systems, or human error.
- Understand Threats: Who might attack and how? (e.g., state-sponsored hackers, ransomware gangs, insider threats).
- Prioritize Risks: Not all risks are equal. Focus on the ones that could cause the most harm.
This ongoing process helps organizations decide where to put their cybersecurity efforts and money. It also helps in understanding information security and its role in cybersecurity.
2. Advanced Threat Intelligence & Continuous Monitoring
Knowing your enemy is half the battle. Aerospace organizations need to constantly gather information about new threats and watch their systems like a hawk.
- Threat Intelligence: Collecting data on the latest attack methods, malware, and hacker groups. This helps predict and prepare for future attacks.
- Security Operations Centers (SOCs): Teams of experts who monitor networks 24/7, looking for suspicious activity.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDPS): Tools that spot and block unauthorized access attempts or malicious traffic.
3. Strong Access Controls & Identity Management
Who can access what? This is critical.
- Least Privilege: Giving users only the access they need to do their job, and no more.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring more than just a password (like a code from your phone) to log in. This makes it much harder for unauthorized users to get in, even if they steal a password.
- Regular Audits: Checking who has access to what and making sure it’s still appropriate.
4. Secure Software Development & Supply Chain Security
Software is everywhere in aerospace, from flight management systems to ground control.
- Security by Design: Building security into software from the very beginning, rather than trying to add it later.
- Regular Testing: Using tools and methods to find and fix bugs or security flaws in software before it’s deployed.
- Supply Chain Audits: Ensuring that all components, hardware, and software from suppliers meet strict security standards. This helps prevent attacks like the one where ICBC Bank faced a ransomware attack through a third-party vendor.
5. Robust Incident Response & Recovery Plans
Even with the best defenses, attacks can happen. Having a plan is key.
- Detection: Quickly spotting when an attack is underway.
- Containment: Stopping the attack from spreading and causing more damage.
- Eradication: Removing the threat from the systems.
- Recovery: Restoring systems and data to normal operation.
- Lessons Learned: Analyzing what happened to improve defenses for the future.
This means practicing these plans regularly, so everyone knows what to do if a real crisis hits.
6. Continuous Training & Awareness
Humans are often the weakest link in cybersecurity.
- Employee Training: Educating all staff, from pilots to ground crew, about cyber threats like phishing scams and how to report suspicious activity. This can help prevent common attacks such as fake job offer scams.
- Specialized Training: Providing advanced training for IT and OT security professionals.
- Culture of Security: Making cybersecurity everyone’s responsibility, not just the IT department’s.
The Role of Regulations and Standards
To ensure a baseline level of security across the industry, various governments and international bodies have put in place strict regulations and standards. These often include:
- Mandatory Security Audits: Regular checks to ensure compliance.
- Reporting Requirements: Forcing organizations to report cyber incidents.
- Certification Programs: Ensuring that certain systems or software meet specific security benchmarks.
These rules help create a common framework for security, pushing all players in the industry to raise their game.
Future Trends and Emerging Threats
The world of cyber threats is always changing. An effective aerospace cybersecurity strategy must look ahead.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): While AI can help with defense, it can also be used by attackers to create more sophisticated attacks. Understanding the impact of AI on the CISO role is crucial.
- Quantum Computing: This emerging technology could potentially break many of today’s encryption methods, requiring a shift to “quantum-safe” cryptography.
- Internet of Things (IoT) in Aviation: More sensors and connected devices on planes and in airports create more potential entry points for attackers.
- Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: These are unknown flaws in software that hackers can exploit before anyone knows they exist. Staying informed about critical vulnerabilities, like CVE-2024-55591, a Fortinet zero-day vulnerability, is vital.
Collaboration is Key
No single company or government can fight cyber threats alone.
- Information Sharing: Aerospace companies, governments, and cybersecurity experts must share threat intelligence and best practices.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Working together to develop new security technologies and strategies.
- International Cooperation: Since aviation is global, international collaboration is essential to create consistent security measures across borders.
Key Summary
The aerospace industry is a cornerstone of our modern world, and keeping it safe from cyber threats is a monumental but absolutely necessary task. A strong, adaptable aerospace cybersecurity strategy is not just about protecting data; it’s about safeguarding lives, ensuring economic stability, and maintaining trust in air travel. By focusing on risk management, advanced threat intelligence, robust controls, secure development, rapid response, and continuous training, the aviation sector can continue to soar safely into the future.














Leave a comment